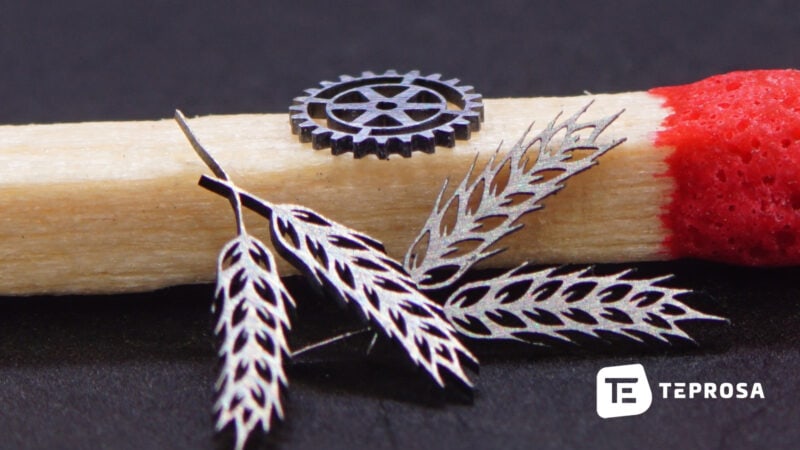
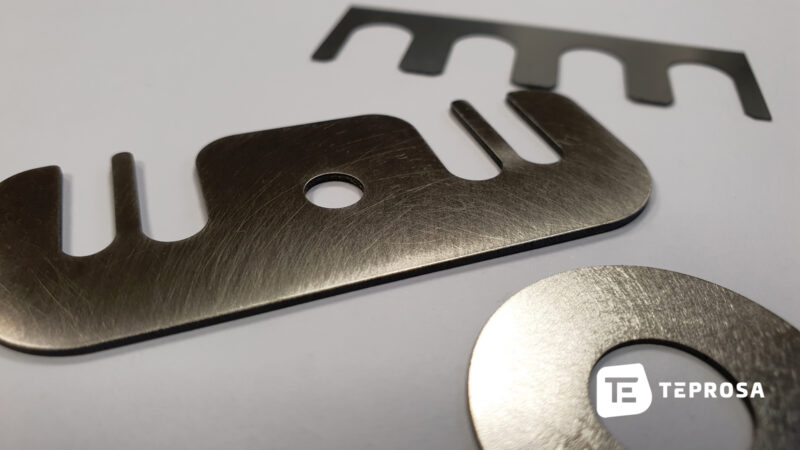
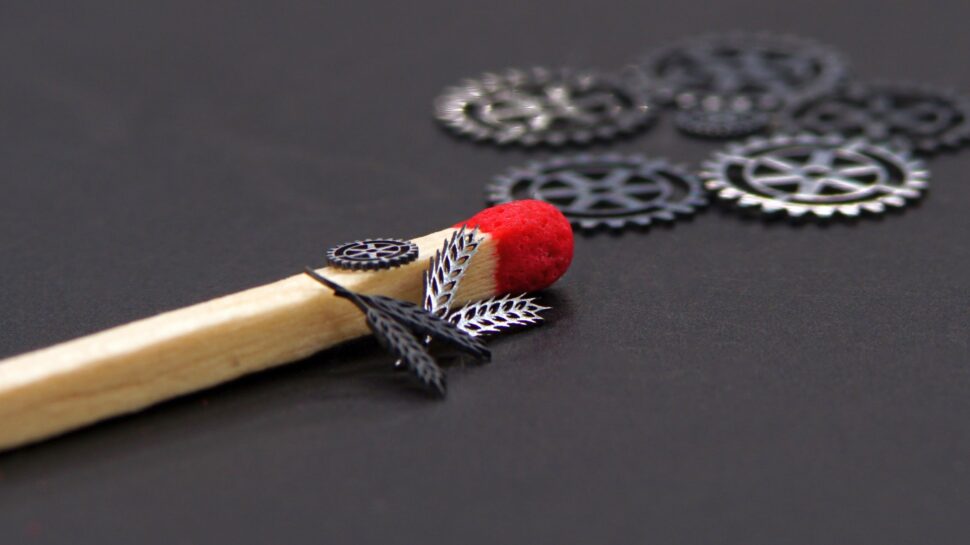
How much does a laser cut cost?
The costs of laser cutting depend on your individual requirements. In the following we want to take a detailed look at the individual factors for the later price of the cuts.
The material
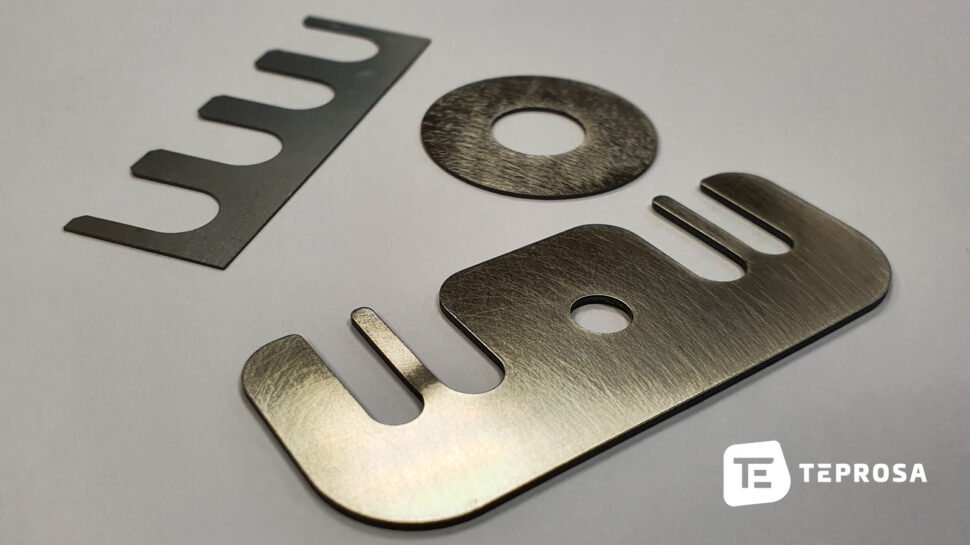
There are many different materials that are suitable for laser cutting. The different materials are also sometimes far apart in price. The selection of a suitable material is not always easy, but it is crucial with regard to the use and the costs of the laser part.
The material thickness
In addition to the cutting speed, the material thickness also determines the time required for the laser beam to pierce the material. Two factors that significantly affect the price.
The cutting speed/feed
Depending on the material and how thick the material to be cut is, the laser can work with a limited cutting speed. Slow speeds automatically mean longer production times and higher costs.
The cutting length
The length of the outer contour of a cutting part results in the cutting length, i.e. the path that the laser has to cover to produce a part. The cutting length is therefore also responsible for the production time.
The part area
The component area determines the material consumption. In the case of particularly unfavorable contours (e.g. circles), the waste can only be optimized to a limited extent.
The cutting accuracy
Basically, higher accuracies require a lower cutting speed. If a higher accuracy of the laser parts is required, the feed with which the laser system works must be reduced.
The complexity of the component
The complexity of a component often has a negative effect on several of the factors mentioned above. For example, a contour with many details and tight curves can mean that the laser has to brake again and again and thus only reaches its maximum speed on a small part of the travel path. A large number of necessary punctures, e.g. in components with many bores, also increases the processing time. A large number of necessary punctures, e.g. in components with many bores, also increases the processing time.
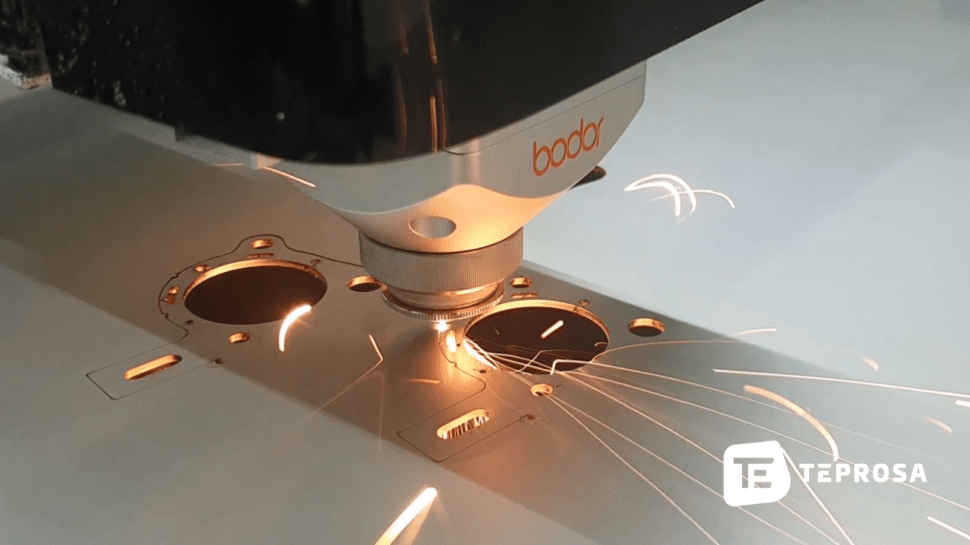
How does laser cutting work?
Like plasma or oxy-fuel cutting, laser cutting is a thermal cutting process. When cutting with the laser, light is bundled into a beam and focused on the material to be cut. The heat generated on the material surface causes the material to melt.
The different cutting processes
Laser cutting is divided into the processes of laser flame cutting, laser fusion cutting and laser sublimation cutting. Depending on the laser process, different process gases are used to support or enhance the cutting process. The basic principle of all processes used in laser cutting with the fiber laser is identical. Nevertheless, each process has its own special characteristics.”
Laser fusion cutting
With laser fusion cutting, the material is melted by a focused laser beam and blown out of the kerf by the cutting gas used. Fusion cutting (also known as laser beam cutting) is the preferred cutting method for machining stainless steel and various aluminum alloys.
The process gas, mostly nitrogen, protects the cutting edge from unwanted oxidation due to its low-reaction properties (inert gas). One also speaks of the gloss cut.
The thermal input to the laser medium is rather low. This results in clean, almost burr-free cut edges and laser parts with almost no distortion or burrs. Post-processing of the parts manufactured in this way is often not necessary.”
laser flame cutting
Oxygen is used as the cutting gas in laser flame cutting (also known as laser beam cutting). In the first step, the material to be processed is heated by the laser beam. In the second step, the cutting gas is blown into the kerf and the material is burned by the supporting effect of the oxygen.
The oxygen fulfills two functions: it reacts with the previously heated material and removes the liquid oxide from the kerf.
Due to the chemical reaction, laser beam flame cutting produces a small amount of burr on the cutting edges, which has to be removed later on thicker foils.”
laser sublimation
With laser sublimation cutting, the material to be processed evaporates immediately as a result of processing with the laser beam. The resulting steam is then blown out by the cutting gas, usually nitrogen. With sublimation cutting, there is no burr on the edges.”
TEPROSA quality
We have set ourselves the goal of manufacturing products of the highest quality. We are ISO 9001 certified and work according to clearly defined processes that we constantly monitor and improve.
For us, quality not only refers to the products, but to all business processes. You can find more information about our quality management system and our processes here.